
















-600x476.jpg)

































-600x476.jpg)
















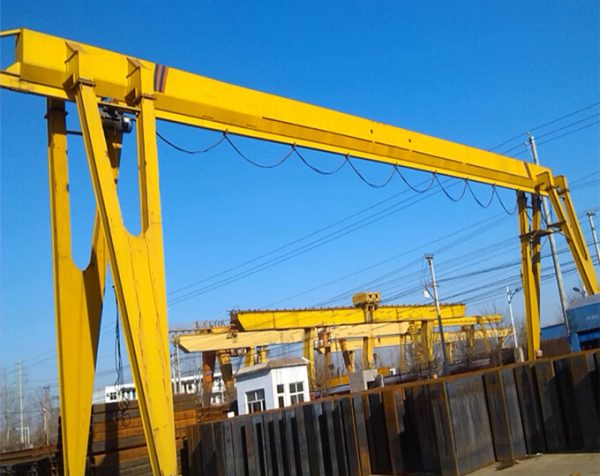
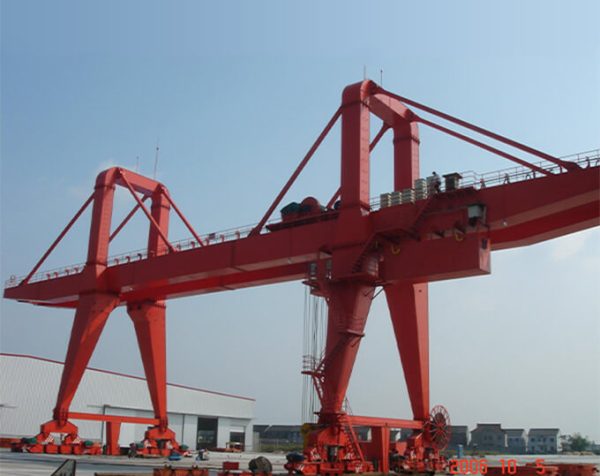
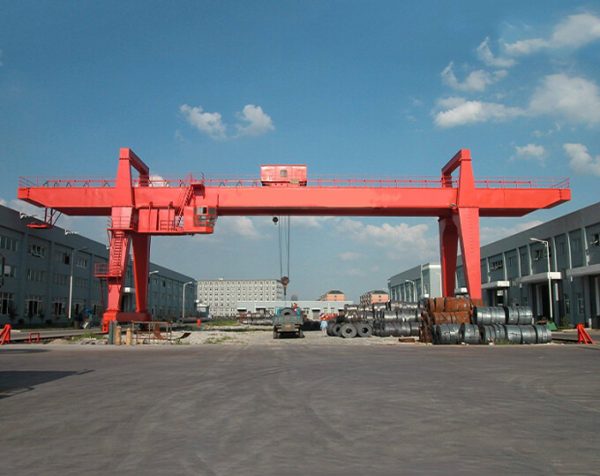
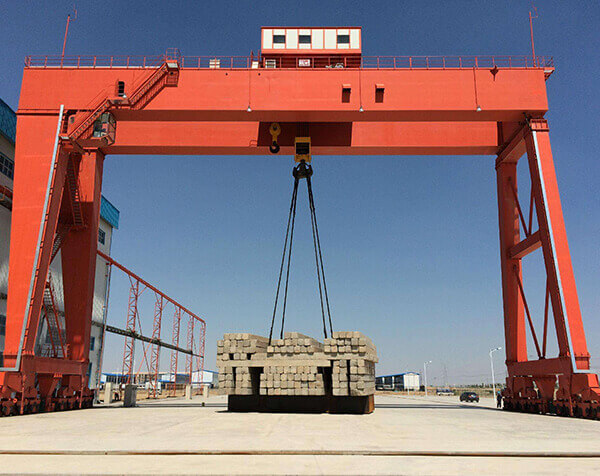
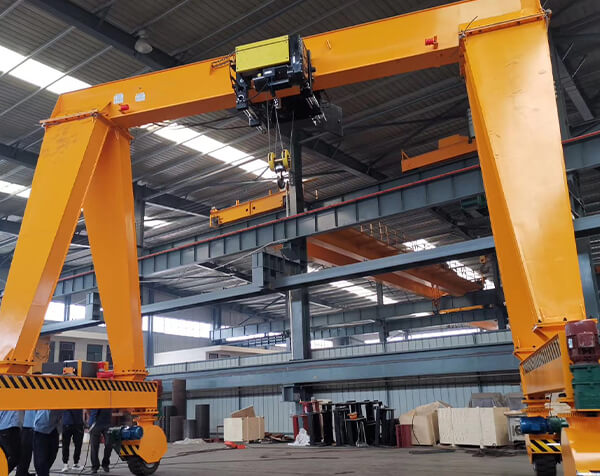
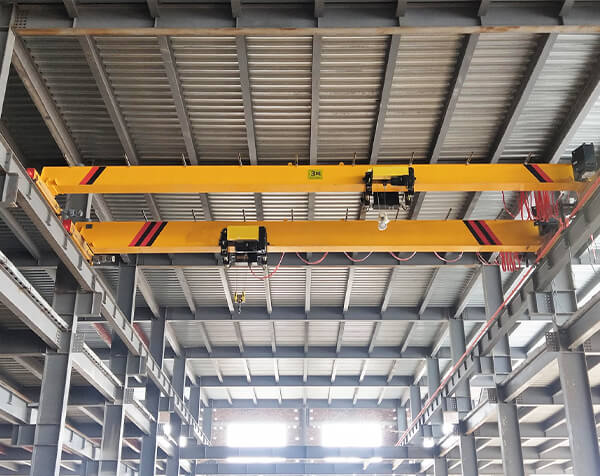
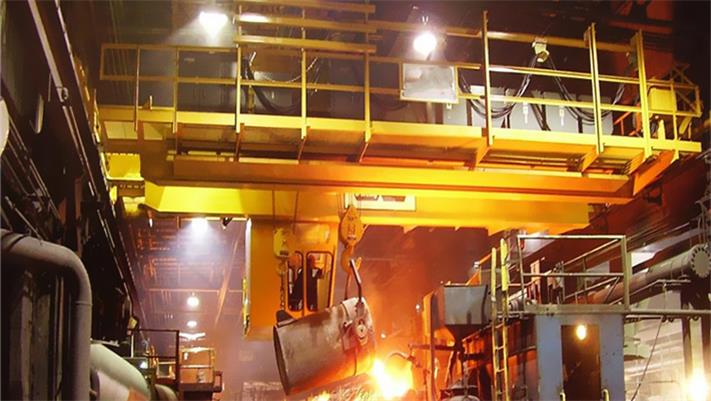
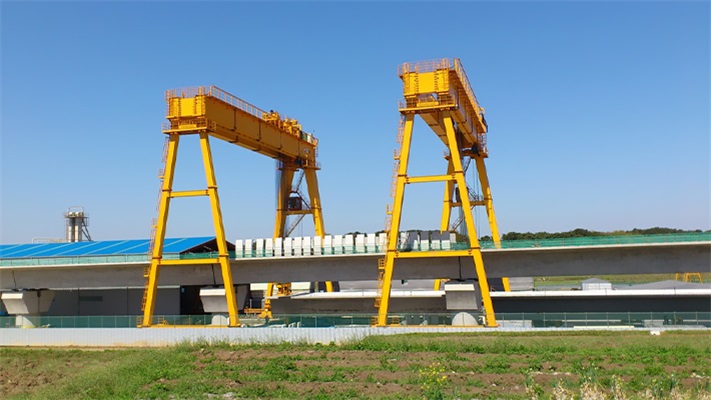
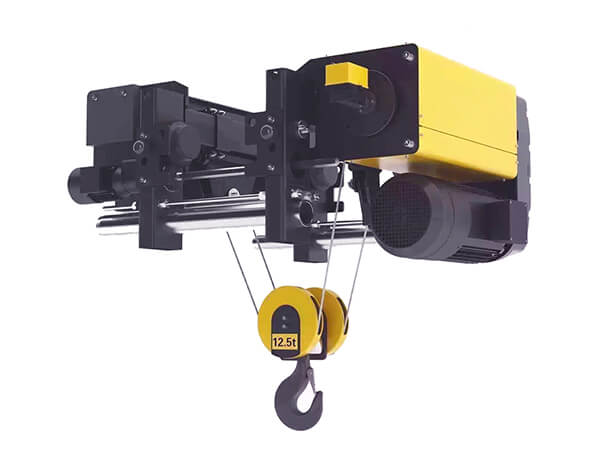
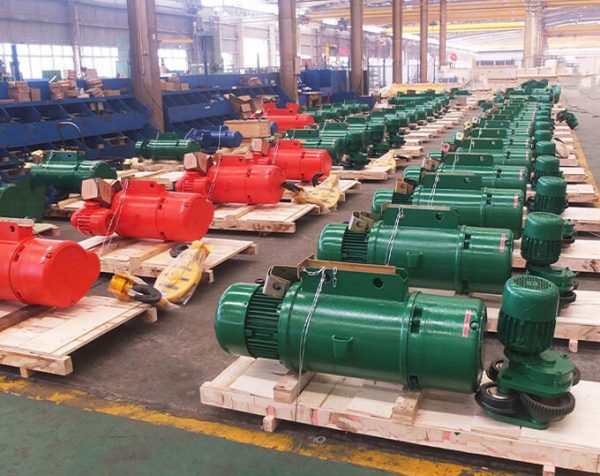
Crane wheels play a critical role in material handling operations. Understanding their design variations helps optimize performance and safety.
Core Elements
Every crane wheel consists of two functional parts:
Material Selection
Manufacturers use different steel grades based on wheel size and application:
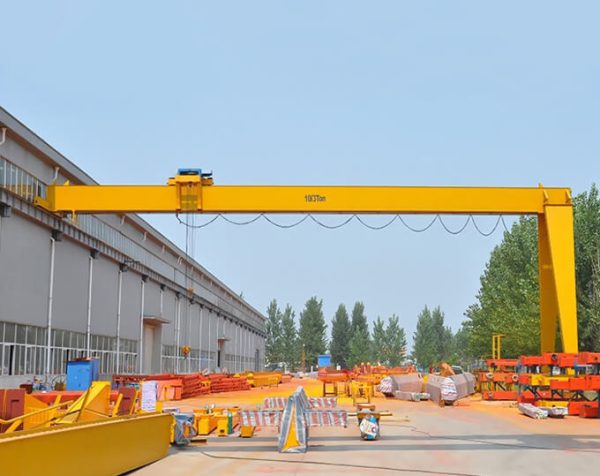
Flange Variations
Crane wheels come in three flange configurations:
Tread Profiles
The contact surface comes in three distinct shapes:
Critical Dimensions
Proper tread width exceeds rail width to accommodate alignment variations:
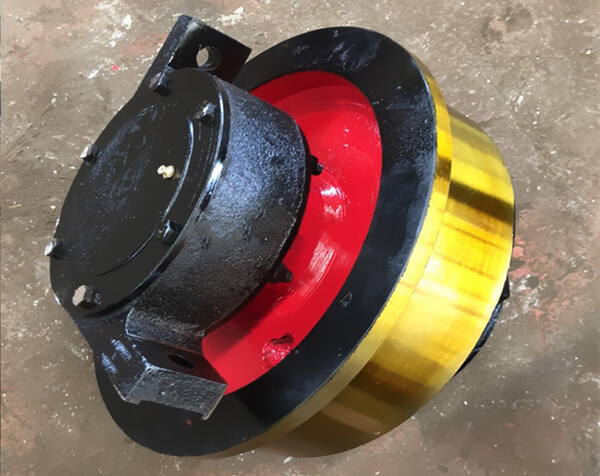


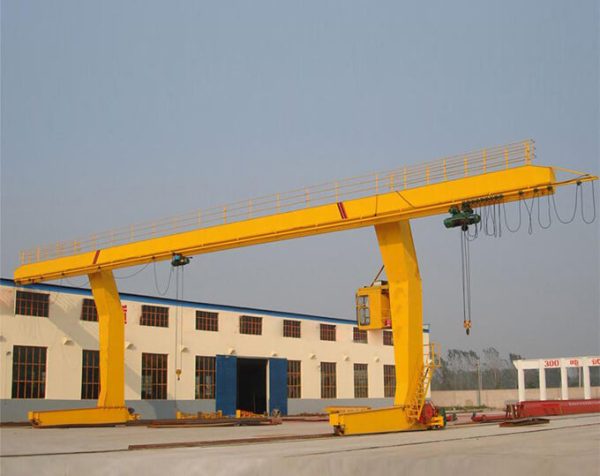
Fixed-Axle Configuration
This traditional design features:
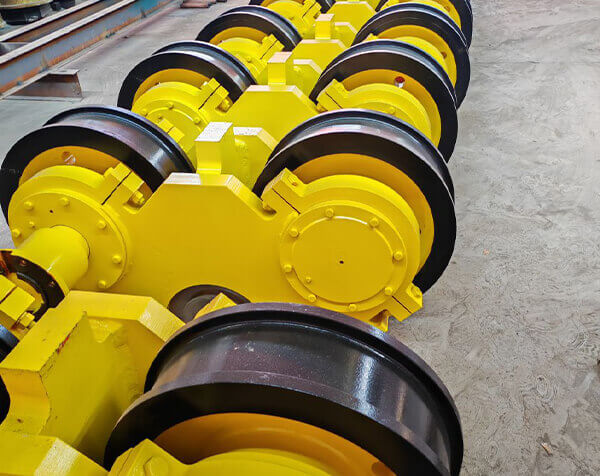
Rotating-Axle Systems
Modern alternatives offer:
Enhanced serviceability despite higher initial cost
Direct shaft rotation for power transmission
Two popular variants: angular bearing housings and split housings
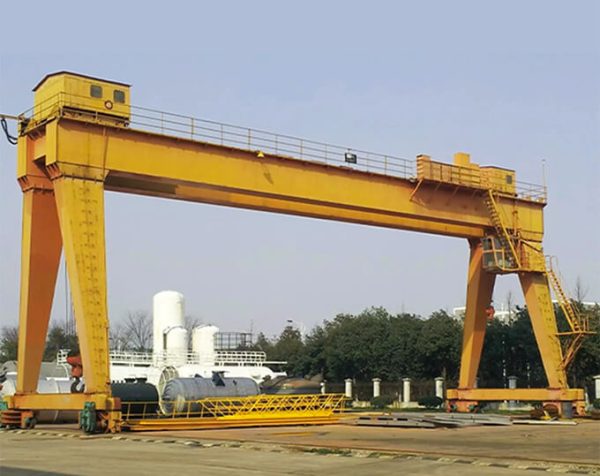
Crane wheels operate on three rail types:
Maintenance Insight
Proper wheel-rail pairing significantly impacts:
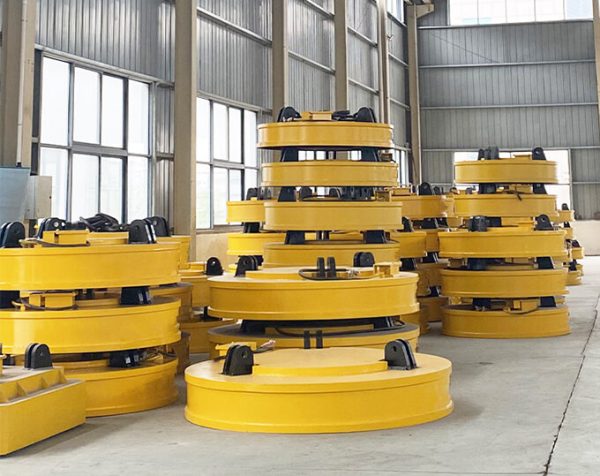
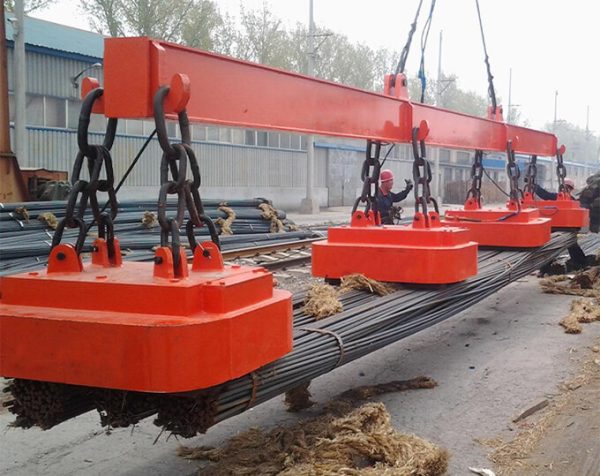
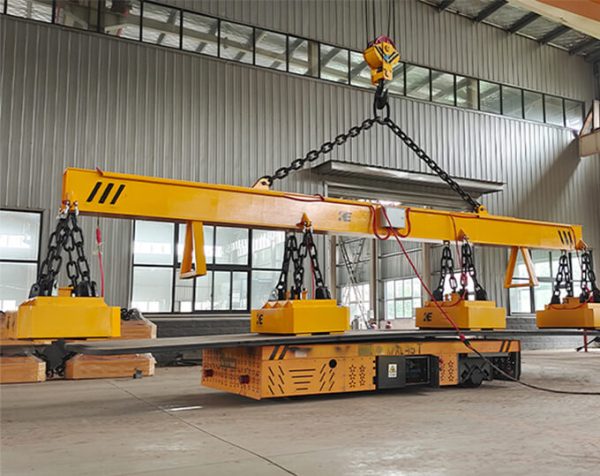
Salvage lifting electromagnet. Its excitation mode can be: constant voltage mode, strong excitation mode and overexcitation mode. The products have different pertinences. Please refer to the selection guide to choose the one suitable for underwater handling of cast iron ingots, steel balls and various scrap steel.
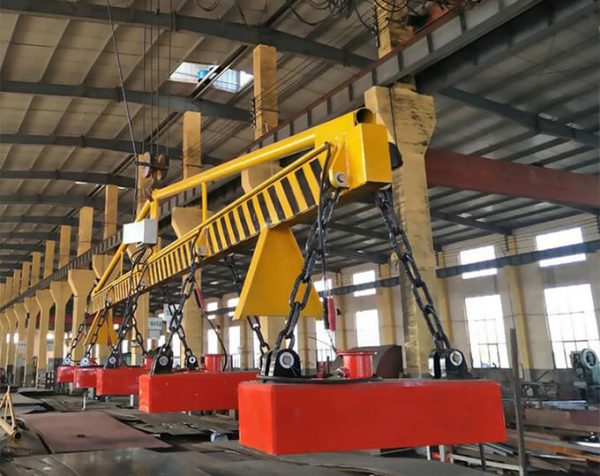
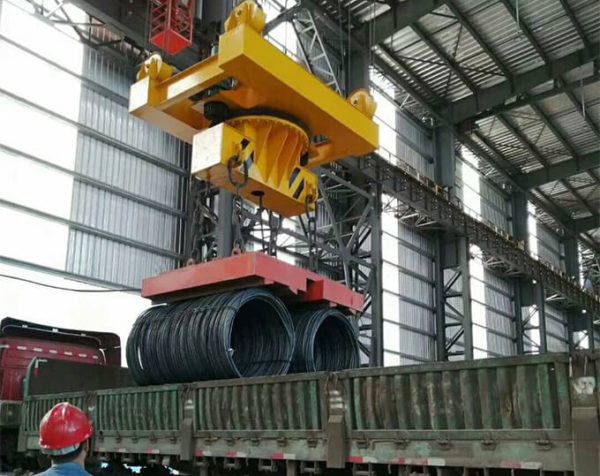
First of all, the electric permanent magnet steel plate spreader is equipped with a battery version, which means that it can carry out up to 500-1000 lifting jobs after a single charge. This undoubtedly provides great convenience for outdoor operations, without relying on power supply, making the operation faster and more efficient.
Crane hooks are very critical components in lifting machinery, which are usually classified according to the materials used, manufacturing processes, uses, and other factors.

